The gut microbiota is a key player involved in health and diseases. Approximately 1014 bacteria and archaea of more than 1,000 species exist in the human gastrointestinal tract; together, these are known as the gut microbiota. The impact of the gut microbiome on health has been a major focus of interest for the past couple of decades, since an adequate gut microbiota and probiotic supplementation have positive effects on many health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and immune and infectious diseases. The role of the gut microbiome in affecting the wellbeing of individuals is encouraging researchers to find new treatments for different health conditions, such as obesity and weight gain. A reciprocated relationship exists between the gut flora and diet, whereby dietary factors regulate the role and structure of the microbiota. of nutrients and have potential consequences on host physiology.
Professor Dr Amandine Everard is assistant professor of Metabolism and Nutrition, researcher from the Belgian Fund for Scientific Research (FNRS) and group leader in the Metabolism and Nutrition lab at the Louvain Drug Research Institute (LDRI) from the UCLouvain, Brussels, Belgium. She is WELBIO investigator (Walloon Excellence in Life Biotechnology). Her main topic of interest in research is to study how gut microbes can impact on metabolic disorders, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes. More specifically, she is investigating the interactions between the gut microbiota, the intestine and the brain in the context of obesity, type 2 diabetes and metabolic diseases.
Title Image credit : Robert W. P. Glowacki, Eric C. Martens, CC BY 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Our guest speaker, Professor Amandine Everard of UCLouvain, shared how she was fascinated early on by the subject of microbiota, which led to her studies of the role the gut microbiome plays in many aspects of our overall health.
Humans co-evolved with bacteria, which is estimated to have first existed approximately four billion years ago. We have 100 trillion living bacteria in our gut, and our body consists of one half microbes and one half human cells. The microbes are 10-50x smaller than human cells, and there are thousands of different species. There are 1-2 kg of microbes in the gastrointestinal tract and colon, and if laid end-to-end these microbes would circle the earth 2.5 times. The intestine is always interacting with microbes, and the interaction should be harmonious.
How does our gut microbiome develop? Are microbes in the womb or developed after birth? This question is somewhat still debated, but it appears that our microbiota develop after birth, and a baby receives their microbiome passing through the vagina of its mother. A baby born via Caesarean section receives it microbes via skin contact and the environment, and by age three the gut microbiome babies become similar. Different microbes exist on different locations of the body, and bacteria names are linked to the type of microbe (ex. staphylococcus). In the past, a sample of bacteria was cultured in a laboratory Petri dish, and then studied with a microscope. It’s estimated that 30% of existing microbes have been studied this way. However, unlike a laboratory, the intestine contains no oxygen, so new tools have been developed. Genome sequencing (using faeces) is now used to find the DNA sequencing of microbes, which has led to the development of identifying the composition of gut microbiota.
Gut microbiota is unique for individuals, similar to fingerprints and barcodes. Therefore, the question is: What is a healthy microbiota? This is a difficult question to answer, and a clear definition does not yet exist, but a high diversity of gut bacteria seems to relate to healthy individuals. Dr. Everard shared information about a study of 100+ people from around the world. In this study, more than 1000 different gut bacteria were discovered, but only 18 bacteria were found to be the same in each person, and these bacteria occurred at different levels.
Photo: Frank Vassen, Wikimedia Commons
These great differences in the gut microbiome exist, and yet patients in the hospital for a disorder are all treated the same – which leads to some having a normal response, some a cautionary, and some a toxic response to treatment. Is there a need to personalize treatment based on the individual’s gut microbiota?
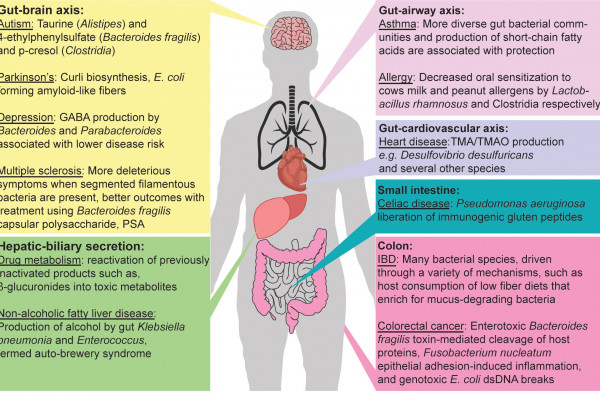
The gut microbiota interacts with the metabolites, hormones, and neurotransmitters of the body. A gut-to-brain axis exists, and is how the microbiota dialogues with the brain. This impacts our eating behaviour (satiety, impulsivity), and various diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, anxiety, depression, appetite disorders) have a correlation to gut microbiota (but not a cause).
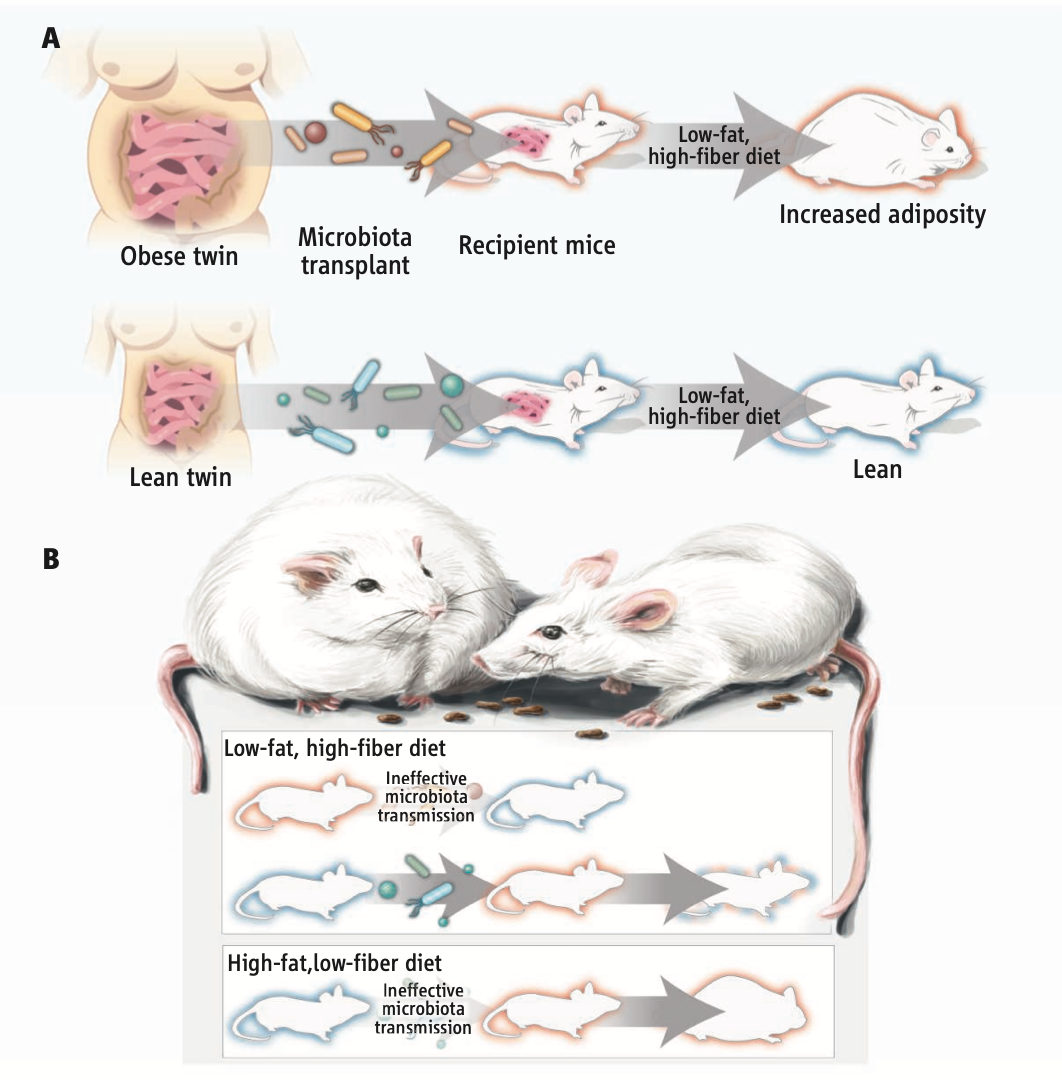
Dr. Everard has focused her study on obesity and its relationship to gut microbiota, and shared the results of a study conducted on mice using human gut microbiota. Mice which were injected with the gut microbiota from obese people led to the mice becoming obese, while that of lean people led to the mice staying lean. Obese individuals tend to have a lower diversity of gut microbiota.
Do tools exist to modify gut microbiota? Dr. Everard identified three:
– fecal matter transplantations
– prebiotics: a substrate that is used as food for the gut’s bacteria (e.g., leeks, onions, garlic, blueberries, asparagus, pomegranate...)
– probiotics: live microorganisms consumed to improve or restore the gut flora (contained in yogurt, sauerkraut, pickles, some cheeses...)
Fecal matter transplantations could be used to combat the serious and sometimes deadly C. difficile, or possibly for diabetics to improve the pathology of the diabetes. But this is not without risk and could transplant pathogens as well, and therefore would require a very focused, methodological approach. Prebiotics can be consumed in fruits and vegetables.
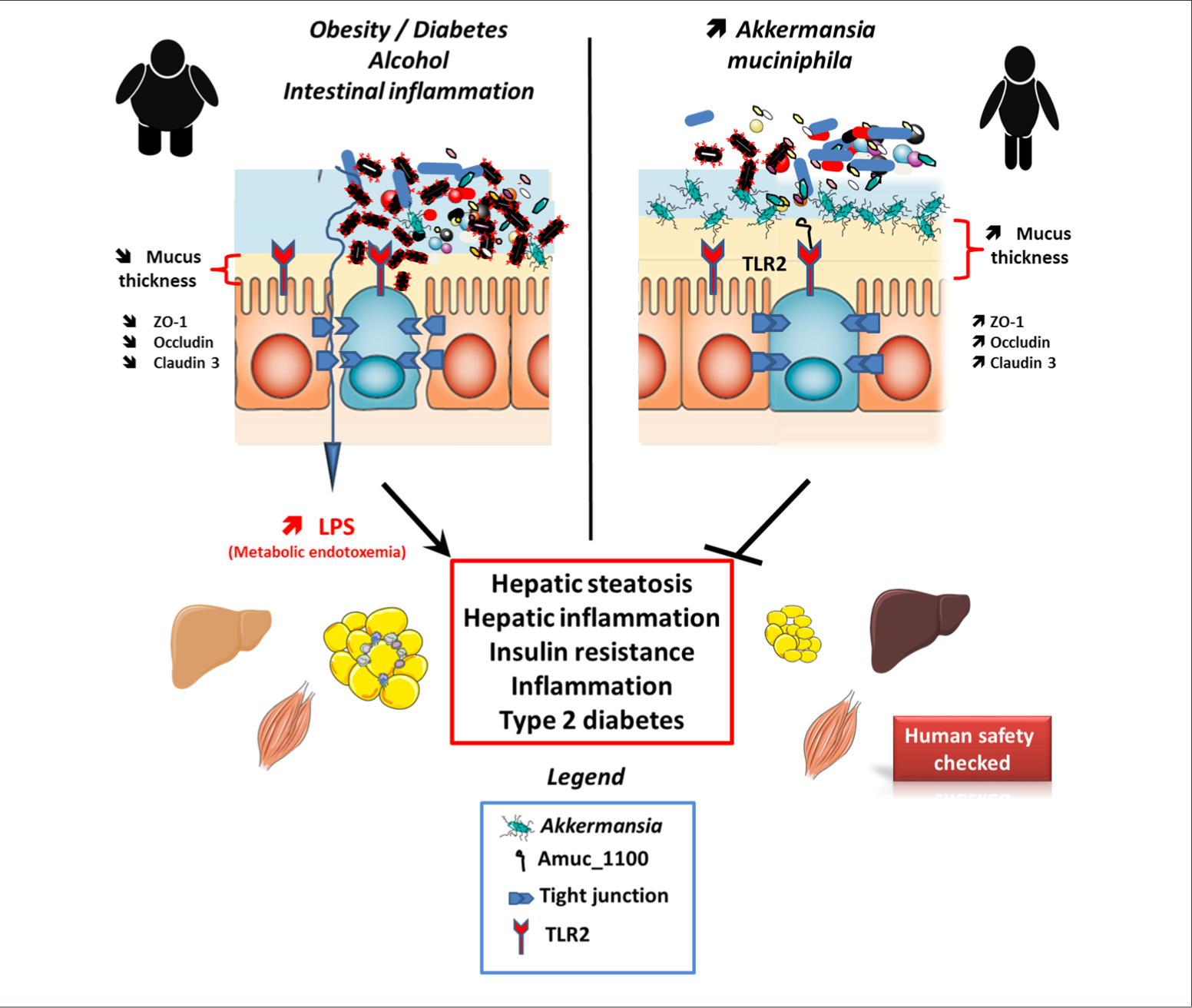
Probiotics appear to be a promising find in the fight against obesity. The amount of the bacteria Akarnania muniniphila (isolated in mucus by Prof. Willem de Vos and Dr. Muriel Derrienfound) increased 80x using a prebiotic treatment. This bacterium has been found to be at lower levels in obese people, but gastric bypass surgery increases the Akkermansia bacteria. And the higher Akkermansia level, the healthier an obese person tends to be. Tests concluded that increasing the level of Akkermansia reduced cholesterol by ten percent, increased insulin sensitivity, and decreased body weight and fat mass in those tested. This was a very encouraging result, but further study and testing must be done.
Dr. Everard concluded her presentation by noting that several next generations, synthetic, beneficial microbes are in the pharmaceutical pipelines, particularly ones acting as a therapeutic for/or prevention of type-2 diabetes and obesity. The challenges for these next generation microbes are efficacy, safety, and industrial production.